Edit Interface
To edit the content of the spreadsheet from your web browser, click on the title of the spreadsheet in the list and then on edit when the spreadsheet page is being displayed. If the spreadsheet is new, it will appear with a single cell (see Fig. 1).
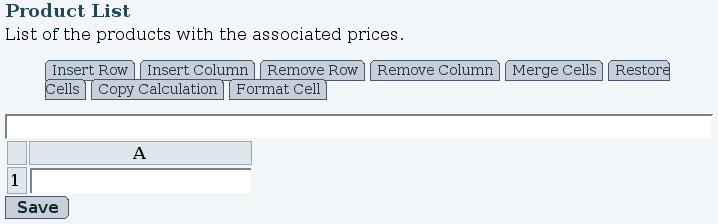
Editing content of a cell
To edit the content of a cell:
- Double-click on the cell
- The current content of the cell appears on the edit bar located at the top of the spreadsheet
- To replace the current content of the cell with something else, just start typing.
- To modify the current content of the cell, click in the edit bar, and modify its content.
- Once your edit is done, press Enter
Modify the Spreadsheet Structure
Multiple options are available to change the structure of the spreadsheet. Here is a summary table.
| Insert Row | Insert one or multiple rows at a specified location | |
| Insert Column | Insert one or multiple columns at a specified location | |
| Remove Row | Delete a single row | |
| Remove Column | Delete a single column | |
| Merge Cells | Merge the selected cells into a single cell | |
| Restore Cells | Unmerge the selected cell to the original state | |
| Copy Calculation | Copy the calculation to an adjacent cell | |
| Format Cell | Applies formatting to a cell (ex.: currency) | |
Columns and rows can be added using the "Insert Row" and "Insert Column" options (see Fig. 2 and Fig. 3). Both will present radio buttons to select if the cells should be added before or after the selected reference. The reference is selected from a combo box listing the row numbers or column letters. A text field is used to specified the amount of items to add.


Note: If you add new rows or columns and save the sheet before entering data into them, Tiki will actually delete the empty rows or columns__.
Columns and rows can be removed one at a time using the "Remove Row" and "Remove Column" options (see Fig. 4 and Fig. 5)


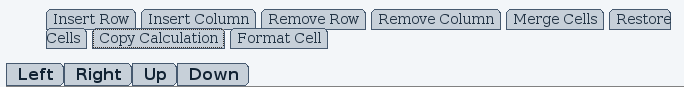
Calculations can be copied across multiple cells using the "Copy Calculation" option (see Fig. 6). Before the direction is selected, the affected cells must be selected. To do so, first select a cell, hold shift and select the last cell. The selected range will be highlighted. In a vertical range where the calculation is written in the first cell, using the "Down" option will copy the calculation in every cell until the end of the range based on the first row.
When the calculation is being copied, the references to other cells are modified to suit the new location. In the example above, the row numbers would increment on every row. Elements in the calculation can be made static. For more information about calculations, see the section on "Calculations and Formulas".
Cell formatting is used to display the numeric values in a different format, such as replacing *2.5* for *$2.50* when displaying currencies. Applying format on a cell does not affect the real value, allowing to perform calculations. The cell formatting can be applied on a range of selected cells using the "Format Cells" option (see Fig. 7).
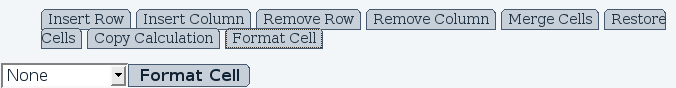
Here is a summary of the available formats available.
| currency | Displays the numeric value with 2 digits precision (ex: 2.00) | |
| currency_us | Displays the numeric value as currency, preceded by dollar sign (ex: $2.00) | |
| currency_ca | Displays the numeric value as currency, apended by dollar sign (ex: 2.00$) | |
Calculations and Formulas
Formulas work in a similar way to those in Excel or OpenOffice.org Calc. Once a cell is selected, a formula can be entered by clicking in the text bar above the spreadsheet and typing *=*, which is the character to indicate the entered value is a formula. Figure 8 contains an example formula.
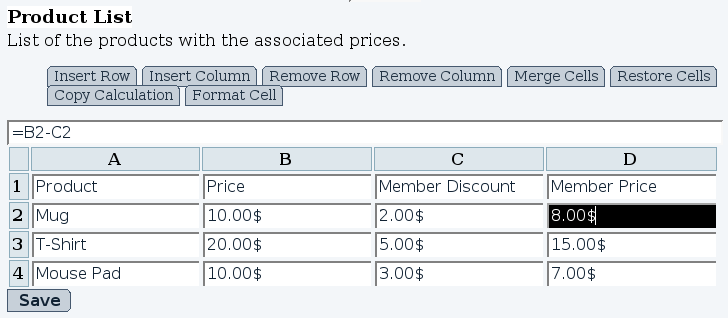
Values from other cells can be included in a formula using the column letter and the row number. The example above substracts the Member discount from the regular price to produce the member price. Most common operators are supported.
Functions can also be used in formulas. Most functions are applied on a range. Ranges can be obtained using A1:Z99 syntax, where the part before the colon is the top left corner of the selection and the part after the colon is the bottom right corner.
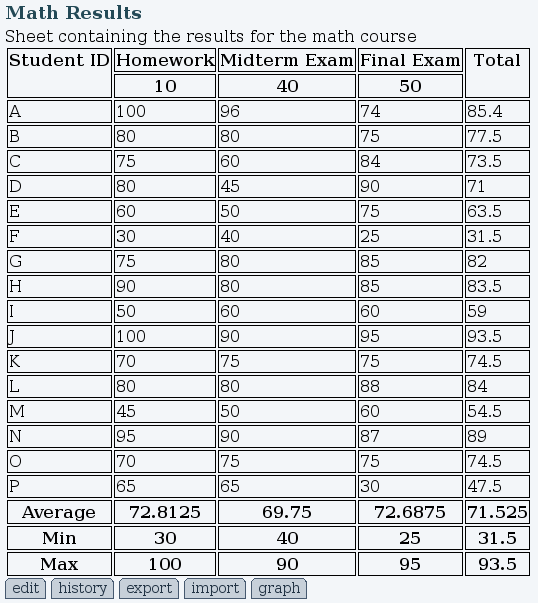
Figure 9 is a sample spreadsheet result. The following formulas have been used to obtain these results:
| Student total result | =B7/100*B$2+C7/100*C$2+D7/100*D$2 | Sum of the obtained results with ponderation |
| Column average | =AVG(B3:B18) | Average of all results in the column |
| Column min | =MIN(B3:B18) | Lesser value in the column |
| Column max | =MAX(B3:B18) | Highest value in the column |
In the student total result, a dollar sign has been added (D$2) in the reference to the field at the top of the page. The dollar sign symbol indicate the value should not be incremented when the calculation is being copied to other cells. Using $D2 would lock the column to D while the row number could increment. Both can be used together ($D$2). As in Excel worksheets, formulas can be replicated in next cells by simply dragging the small square icon at the bottom-left corner of a cell. The corresponding free cells (not locked by $) will change accordingly.
A range can also be created using brackets. For example, a range containing cells from A1 to A4, excluding A2 could be created using: [ A1, A3, A4 ] .
Here is a list of the functions available:
| SQRT( val ) | Square root of val | |
| MIN( range ) | Finds the lesser value in range | |
| MAX( range ) | Finds the largest value in range | |
| SUM( range ) | Sums all values in range | |
| AVG( range ) | Average value in range | |
| SUMIF( testRange, val or range, sumRange ) | Sum of elements in sumRange if matching value in testRange is equal to val or any value in range | |
Math methods
Because the spreadsheet is implemented using Javascript, the Math object's methods can be used. For example, Math.round() will round to the nearest integer. This use is more fragile than native TikiWiki functions, and these methods should be added to the spreadsheet functions in the future.
| abs | Returns the absolute value of a number. | |
| acos | Returns the arccosine (in radians) of a number. | |
| asin | Returns the arcsine (in radians) of a number. | |
| atan | Returns the arctangent (in radians) of a number. | |
| atan2 | Returns the arctangent of the quotient of its arguments. | |
| ceil | Returns the smallest integer greater than or equal to a number. | |
| cos | Returns the cosine of a number. | |
| exp | Returns Enumber, where number is the argument, and E is Euler's constant, the base of the natural logarithm. | |
| floor | Returns the largest integer less than or equal to a number. | |
| log | Returns the natural logarithm (base E) of a number. | |
| max | Returns the largest of zero or more numbers. | |
| min | Returns the smallest of zero or more numbers. | |
| pow | Returns base to the exponent power, that is, base exponent. | |
| random | Returns a pseudo-random number between 0 and 1. | |
| round | Returns the value of a number rounded to the nearest integer. | |
| sin | Returns the sine of a number. | |
| sqrt | Returns the square root of a number. | |
| tan | Returns the tangent of a number. | |